
Heart Cut History
The exact origins of the heart brilliant are unknown although being a modified brilliant cut it may have appeared as early as the 16th century. However, gems which would today be classified as ‘triangular with rounded corners’ or ‘drops’ were at one time described as being heart-shaped. Indeed, this is evident from the many descriptions in French inventories dating from the middle of the seventeenth century. The first recorded heart shape diamond appears in a portrait entitled "The Gonzaga Princess,” painted circa 1605 by Frans Pourbus the younger. The large piece of jewellery on the princess’s left sleeve contains a variety of different cuts, some of which are thought to be versions of the heart-like ‘drops’ popular in France at the time. The heart shape is also mentioned in a book written in 1655 by Jean-Baptiste Tavernier, the French merchant-traveller who found his fortune in the precious stone trade and famously brought the Hope Diamond to France. In the text, he recalls seeing the “Heart Diamond,” a 36-carat heart-shaped brilliant in an ornament in the treasure of Aurangzeb, in India.
Features
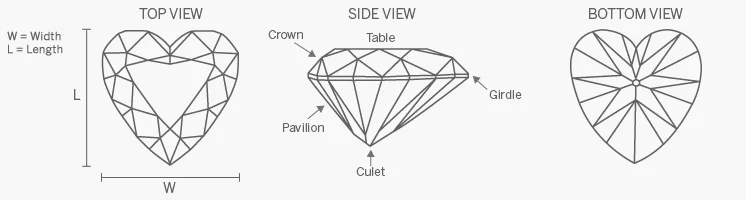
The heart shape is usually comprised of between 56 and 58 facets, although the number of main pavilion facets may vary between 6, 7 and 8. Additionally, heart shapes are sometimes cut with “French tips,” which replace the large bezel facet at the point with star and upper girdle facets. French tips are also used in the Marquise and Pear shapes. Heart shapes may differ slightly in appearance depending on their make or structure.
The traditional heart shape should have a ratio between 0.90 and 1.10 and be absolutely symmetrical with the lobes (top arches) of even height and breadth, although these specifications may be altered according to personal preferences.
In determining the length to width ratio for heart shapes, the width is measured at the widest point of the shape from the edge of one lobe to the other. In addition, the heart shape can suffer from a so-called “bow-tie effect” when light passing through the diamond casts a shadow across the central facets of the stone.
Proportions
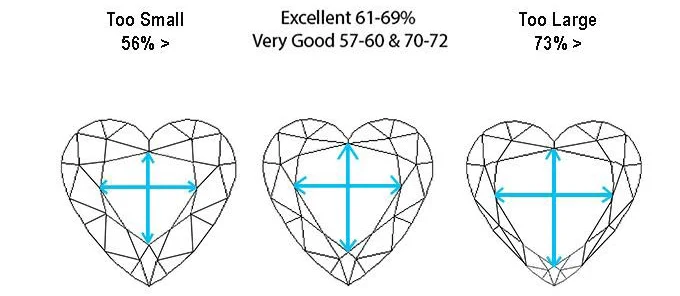
Heart diamonds don’t officially have a cut grade. However, there are a few guidelines that will assist you when it comes to choosing a heart shaped diamond.
| Heart Cut | Excellent | Very Good | Good |
|---|---|---|---|
| Table % | 55% - 62% | 53% – 64% | 52% – 65% |
| Depth % | 52% – 60% | 50% – 62% | 45% – 65% |
| Polish/Symmetry | Good to Excellent | ||
| Ratio (L/W) | 0.90 - 1.10 | 0.85 - 1.20 | |


 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 中文
中文